Click, Cart, and Conquer: Mastering the Art of Online Selling

The evolution of e-commerce solutions has brought about a notable transformation in the swiftly expanding realm of digital commerce. Transitioning from the initial phase of online marketplaces to the contemporary era marked by state-of-the-art technologies, businesses have employed diverse strategies to engage customers and streamline transactions. Many factors have influenced this extraordinary path, including evolving customer expectations, technological advancements, and the never-ending search for more efficient and personalized online experiences. This investigation aims to dissect the fundamental elements and patterns that characterize successful e-commerce solutions, emphasizing their pivotal function in molding the trajectory of trade and customer relations in the future.
The Evolution of E-commerce Solutions:
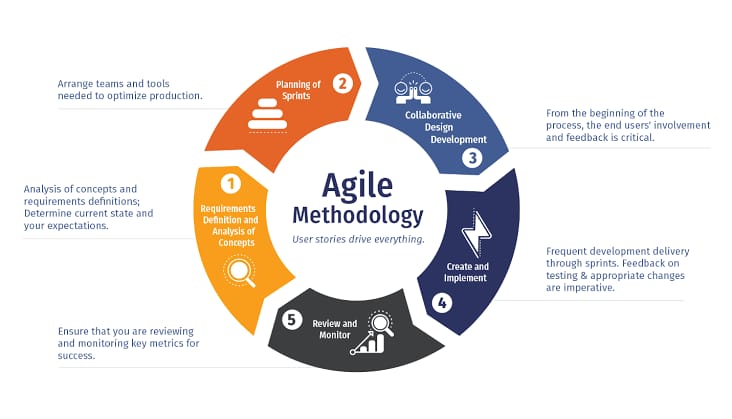
Technological developments, shifting consumer habits, and shifting corporate environments have all influenced the dynamic and revolutionary evolution of e-commerce solutions. The following provides a timeline of significant turning points and patterns in the development of e-commerce solutions:
Early Years (1990s):
- Emergence of Online Shopping: The concept of online shopping began with the development of early e-commerce platforms like Amazon and eBay.
- Basic Websites: Initially, e-commerce websites were basic and focused on individual product pages with simple checkout processes.
Dot-com Boom (late 1990s):
- Proliferation of E-commerce firms: With businesses experimenting with new technology and business strategies, e-commerce firms proliferated during the dot-com boom.
- Difficulties and Setbacks: A lot of new businesses had difficulties, and some failed because of overvaluation and unviable business plans.
- E-commerce Platforms (early 2000s):
- The emergence of e-commerce platforms such as Magento, Shopify, and WooCommerce in the early 2000s provided businesses of all sizes with customisable options.
- Payment Options: The whole online buying experience was enhanced by the addition of safe payment options like PayPal and other gateways.
Mobile Commerce (mid-2000s to 2010s):
- Mobile Optimization: The advent of smartphones led to the optimization of e-commerce websites for mobile devices, giving rise to mobile commerce (m-commerce).
- Mobile Apps: Retailers began developing mobile apps to provide a more seamless and personalized shopping experience.
- Social Commerce (2010s):
- Integration with Social Media: E-commerce systems have begun to integrate with social media platforms, enabling consumers to find and buy things directly through Facebook, Instagram, and other platforms.
- Influencer Marketing: Sales via social media platforms were greatly aided by the emergence of influencer marketing.
Omnichannel Commerce (2010s):
- Integration of Offline and Online Channels: Businesses adopted omnichannel strategies, integrating their online and offline sales channels for a cohesive customer experience.
- Buy Online, Pick Up In Store (BOPIS): Retailers introduced BOPIS services, allowing customers to order online and pick up their purchases in physical stores.
- Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR):AR for Check-Ons: A few e-commerce sites have used augmented reality technology to let users virtually try on items like apparel and accessories.
- VR for Virtual Shopping: VR experiences were introduced to create virtual shopping environments, enhancing the immersive aspect of online shopping.
- Blockchain and Cryptocurrency (late 2010s to 2020s):
- Blockchain for Security: Blockchain technology was explored for enhancing security in e-commerce transactions, providing transparent and secure payment processes.
- Cryptocurrency Payments: Some e-commerce platforms began accepting cryptocurrency payments, offering an alternative to traditional payment methods.
Sustainability and Ethical Commerce (2020s):
- Focus on Sustainability: E-commerce businesses increasingly emphasized sustainability and ethical practices, responding to consumer demand for environmentally friendly and socially responsible products.
- Circular Economy Initiatives: Some platforms introduced initiatives to promote a circular economy, including recycling programs and product life cycle management.
- New Technologies and Trends (ongoing):
- Voice Commerce: Using voice instructions, customers can make purchases using voice commerce. The emergence of virtual assistants and voice-activated gadgets made it feasible.
- Edge Computing: By reducing transaction latency in e-commerce, edge computing research seeks to increase the efficiency and speed of online shopping.
Types of E-commerce Solutions:
Diverse sorts of e-commerce solutions are available to meet the needs of diverse industries, business models, and customers. These are a few typical categories of online storefronts:
- B2C, or business-to-consumer: B2C e-commerce involves transactions between businesses and individual consumers. It is the most typical kind of online shopping. An illustration would be online retailers like Amazon, where customers buy goods straight from the internet.
- B2B (business-to-business): B2B e-commerce involves transactions between businesses. It includes wholesale trade, where businesses buy and sell products or services to each other. Alibaba is an example of a platform that links merchants and enterprises with manufacturers and distributors.
- Consumer-to-consumer, or C2C, e-commerce refers to transactions that take place between individual customers. Online marketplaces make it easier to acquire and sell goods and services by serving as middlemen. Websites like eBay and Craigslist allow users to sell both new and used goods to other users.
- Companies to Companies (C2B): The process by which individual consumers sell products or services to businesses is known as C2B e-commerce. freelance marketplaces such as Fiverr and Upwork, where people sell their talents or abilities to companies.
- Mobile Commerce (M-Commerce): M-commerce is the practice of conducting online business using mobile devices, like tablets and smartphones. Examples include e-commerce platform mobile websites or applications for shopping on the go.
- Social Commerce: Product discovery and purchase are made possible through the direct integration of e-commerce with social media platforms, known as social commerce. Instagram Shopping, where users can explore and buy products showcased on Instagram.
- Voice Commerce: Voice commerce enables users to make purchases using voice commands through virtual assistants or voice-activated devices. Voice-activated shopping through devices like Amazon Echo or Google Home.
- Omnichannel Commerce: Omnichannel commerce provides a seamless and integrated shopping experience across various channels, including online and offline. Buy Online, Pick Up In Store (BOPIS) services, where customers can order online and pick up their purchases at a physical store.
- Dropshipping: Dropshipping is a retail fulfillment strategy in which a store sells things without maintaining inventory. As an alternative, you buy the product from a third party and ship it straight to the consumer when you sell something. Shopify stores that source products from suppliers and send them straight to customers are an example of dropshipping models in action.
- Subscription E-commerce: Subscription e-commerce involves selling products or services on a recurring basis, typically through subscription plans. Subscription boxes like Birchbox or services like Netflix, where customers pay regularly for access to products or content.
- Green (Sustainable) E-commerce: This type of online shopping emphasizes socially conscious and ecologically friendly business methods. e-commerce sites that prioritize sustainable packaging, ethical sourcing, and environmentally friendly products.
- Blockchain-Based E-Commerce: This type of online shopping makes use of blockchain technology to ensure safe and transparent transactions.. Platforms using blockchain for secure payment processing or tracking the supply chain of products.
Key Components of Effective E-commerce Solutions:
User-Friendly Website Design:
- Responsive Design: A website that is both aesthetically pleasing and easily navigable on a variety of devices, such as computers, tablets, and smartphones, is said to have responsive design.
- Intuitive Navigation: Easy navigation and a clear layout help users find products and information quickly.
Product Catalog and Management:
- Comprehensive Product Listings: Well-organized product catalogs with detailed descriptions, high-quality images, and relevant information.
- Inventory Management: Efficient tracking and management of product availability, preventing overselling and stockouts.
Shopping Cart and Checkout Process:
- Streamlined Checkout: A simplified and user-friendly checkout process with minimal steps to reduce cart abandonment.
- Guest Checkout Option: Allow customers to make purchases without creating an account, enhancing convenience.
Order Management System:
- Order Tracking: Real-time order tracking for customers to monitor the status of their purchases.
- Automated Order Processing: Efficient systems for order confirmation, processing, and fulfillment.
- Customer Accounts and Profiles:
- User Registration: Optional account creation for personalized experiences and order history tracking.
- Profile Customization: Allow users to manage preferences, addresses, and payment information.
- Customer Support and Communication:
- Live Chat and Chatbots: Real-time customer support through live chat or automated chatbots.
- Email Notifications: Automated emails for order confirmations, shipping updates, and customer feedback.
Security Measures:
- SSL Certificates: Secure connections with SSL certificates to encrypt data transmission.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) Compliance: Adherence to security standards for handling payment information.
Search and Filtering Capabilities:
- Robust Search Functionality: Advanced search options for users to easily find products.
- Filtering and Sorting: Options to filter and sort products based on various criteria.
Mobile Optimization:
- Responsive Design: Ensuring the website is optimized for a seamless mobile shopping experience.
- Mobile Apps: Developing mobile applications for platforms like iOS and Android.
Analytics and Reporting:
- Data Analytics: Utilizing analytics tools to track user behavior, sales performance, and website traffic.
- Reporting Features: Generating reports for insights into key metrics and trends.
Integration with Third-Party Services:
- Payment Processors: Integration with secure and reliable payment gateways.
- Shipping and Logistics: Integration with shipping carriers for accurate shipping rates and tracking.
Social Media Integration:
- Social Sharing: Integration with social media platforms for easy sharing of products.
Enabling people to sign in with their social networking credentials is known as social login.
Performance & Scalability:
- Scalable Architecture: Building an infrastructure that can handle increased traffic and growth.
- Fast Loading Times: Optimizing website performance for quick page loading.
Legal Compliance:
Complying with data protection laws, such the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), is known as GDPR compliance.
- E-commerce Laws: Adhering to national and worldwide e-commerce statutes and guidelines.
PageCraft: Elevating Sales with High-Converting Product Pages
a. Compelling Product Descriptions:
- Craft detailed yet concise product descriptions.
- Highlight key features and benefits.
- Use persuasive language to create a sense of urgency or exclusivity.
b. High-Quality Images and Videos:
- Include clear, high-resolution images from different angles.
- Use videos to demonstrate product use and benefits.
- Implement zoom features for a closer look at products.
c. Customer Reviews and Testimonials:
- Display genuine customer reviews and testimonials.
- Encourage customers to leave feedback through follow-up emails.
- Showcase positive reviews prominently on the product page.
d. Clear Call-to-Action (CTA):
- Design prominent and visually appealing CTAs.
- Use action-oriented phrases like "Buy Now" or "Shop Today."
- Ensure easy navigation from product page to checkout.
e. Mobile Optimization:
- Ensure the product page is optimized for mobile devices.
- Implement responsive design for seamless mobile user experience.
- Check loading times on different devices and optimize accordingly.
Smooth Sailing: Mastering Checkout Optimization to Slash Abandonment Rates
a. Streamlined Checkout Flow:
- Minimize the number of steps in the checkout process.
- Implement a guest checkout option for users who don't want to create accounts.
- Use progress indicators to show users where they are in the checkout process.
b. Transparent Pricing and Policies:
- Clearly display product prices and any additional costs.
- Provide shipping information upfront.
- Be transparent about return and refund policies.
c. Multiple Payment Options:
- Offer various payment methods to cater to different preferences.
- Ensure secure payment gateways are in place.
- Clearly communicate the security of payment processes.
d. Abandoned Cart Recovery:
- Implement email reminders for abandoned carts.
- Incentivize users to complete the purchase with discounts or promotions.
- Analyze data to understand common reasons for cart abandonment and address them.
Fortify & Thrive: Unveiling Security Measures for E-commerce Fortresses
a. SSL Encryption:
Use SSL certificates to encrypt data transmitted between the user and the website.
- Display security badges to build trust.
b. Secure Payment Gateways:
- Choose reputable and secure payment gateways.
- Regularly update and patch payment processing software.
c. Data Protection and Privacy:
- Comply with data protection regulations.
- Clearly communicate your privacy policy to users.
- Secure customer data and regularly audit security protocols.
d. Two-Factor Authentication:
- Implement two-factor authentication for customer accounts.
- Provide account recovery options for added security.
- AI Elevation: Revolutionizing E-commerce with Personalized Recommendations
a. User Behavior Analysis:
- Use AI algorithms to analyze user behavior on the website.
- Understand browsing patterns, preferences, and purchase history.
b. Personalized Product Recommendations:
- Implement personalized product suggestions based on user history.
- Use AI to analyze real-time data and adapt recommendations.
c. Chatbots for Customer Support:
- Integrate AI-powered chatbots for instant customer support.
- Provide personalized assistance and product recommendations through chatbots.
d. Dynamic Pricing:
- Use AI to adjust prices dynamically based on demand, inventory, and user behavior.
- Implement personalized discounts and promotions.
e. Email Personalization:
- Utilize AI to personalize email marketing campaigns.
- Send targeted product recommendations and exclusive offers based on user preferences.
In conclusion, the evolution of e-commerce solutions has been a dynamic process propelled by shifts in consumer behavior, technological breakthroughs, and business adaptation to a constantly shifting digital environment. From the early days of online shopping to the current era of sophisticated AI-driven experiences, e-commerce solutions have consistently evolved to meet the diverse needs of both businesses and customers. The key components of effective e-commerce systems, like user-friendly design, secure payment gateways, quick checkout processes, and advanced analytics, support online enterprises. Future e-commerce chapters will probably be shaped by the continued integration of developing technology, an emphasis on sustainability, and the smooth blending of online and physical channels. In an increasingly linked digital world, e-commerce solutions will continue to be essential in transforming the way we purchase and sell by offering accessibility, convenience, and personalization.
Recent Stories
500k Customer Have
Build a stunning site today.
We help our clients succeed by creating brand identities.
Get a Quote