Mobile-Optimized Navigation Patterns

Versatile upgraded route designs stand at the front of current computerized plans, answering the developing scene of portable perusing and client conduct. As the commonness of cell phones keeps on rising, guaranteeing a consistent and natural route on more modest screens has become principal for architects and engineers. Versatile upgraded route designs envelop a different scope of methods and systems pointed toward working on client collaboration, smoothing out admittance to content, and improving by and large convenience on cell phones. From responsive menus and burger symbols to base route bars and motion based controls, these examples are fastidiously created to oblige the imperatives of portable connection points while keeping up with usefulness and tasteful allure. By focusing on portable streamlined routes, originators can make encounters that reverberate with clients, encouraging commitment, fulfillment, and at last, progress in the versatile first advanced scene.
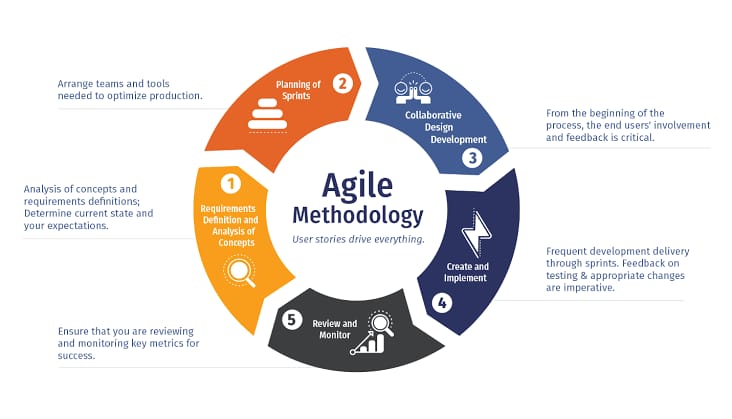
Exploring the Versatile Scene
Exploring the versatile scene includes understanding the elements of the quickly developing portable innovation industry. Consider these important points:
- Stage Variety: Cell phones run on different working frameworks, with Android and iOS being the predominant ones. Every stage has its own arrangement of improvement devices, rules, and client ways of behaving. Understanding these distinctions is urgent for application engineers and advertisers.
- Client Experience (UX): Versatile clients have elevated standards for consistent and natural encounters. Planning versatile connection points with an emphasis on straightforwardness, responsiveness, and openness is fundamental for progress.
- Application Advancement: The portable application market is exceptionally serious. Engineers should remain refreshed on the most recent advancements, systems, and programming dialects to make inventive and excellent applications. For creating apps that function on a variety of platforms, cross-platform development tools like Flutter and React Native have gained popularity.
- Application Adaptation: There are different adaptation techniques for portable applications, including freemium models, in-application buys, memberships, and promotions. Picking the right adaptation system relies upon factors like the ideal interest group, application specialty, and client commitment.
- Application Showcasing: To stand out from the crowd of millions of apps in the app stores, effective marketing strategies are required. Application store enhancement (ASO), web-based entertainment showcasing, force to be reckoned with organizations, and designated promoting are normal strategies used to increment application perceivability and downloads.
- Portable Web versus Local Applications: Organizations should choose whether to foster a local versatile application or streamline their site for portable programs. Each approach has its potential gains and disadvantages, dependent upon factors like monetary arrangement, vested party, and required features.
- Emerging Progressions: Progressions like expanded reality (AR), increased reality (VR), man-made cognizance (PC based insight), and the Trap of Things (IoT) are framing the destiny of flexible advancement. Watching out for these patterns and investigating how they can improve versatile encounters is critical to remaining ahead in the portable scene.
- Information Protection and Security: With expanding worries about information protection and security, versatile application engineers should focus on carrying out hearty safety efforts and conforming to guidelines like GDPR and CCPA to safeguard client information.
By remaining informed about these perspectives and constantly adjusting to changes in the versatile scene, organizations can actually explore the portable environment and profit by amazing open doors for development and advancement.
Key Standards of Portable Route Plan
Viable portable route configuration assumes a basic part in guaranteeing a consistent and natural client experience. The following are a couple of crucial norms to consider:
- Simplicity: To avoid confusing users with too many options, keep navigation menus uncluttered and simple. Limit the quantity of things in the route menu and focus on the main ones.
- Consistency: Keep up with consistency in route components across all screens of the application or site. To make it easier for users to quickly understand how to use the interface, make use of familiar icons, labels, and placements.
- Clear Structure: Lay out a reasonable pecking order of route components in light of the significance of content and client undertakings. Utilize obvious signals like size, variety, and arrangement to show the order and guide clients through the route stream.
- Visibility: Make sure that all sizes of screens can easily see and reach the navigation elements. Utilize conspicuous situations, differentiating colors, and unmistakable symbols to cause you to notice the route menu.
- Responsive Plan: Plan route menus that adjust to various screen sizes and directions. To ensure that navigation elements remain usable and accessible on all devices, including smartphones and tablets, employ responsive design techniques.
- Thumb-Accommodating Plan: Think about how mobile devices feel to use, and make navigation elements that are easy to reach and use with the thumb. Place significant route things inside simple reach of the client's thumb to limit strain and further develop ease of use.
- Logical Route: Give logically pertinent route choices in light of the client's ongoing area inside the application or site. Use breadcrumbs, back buttons, and logical menus to help clients explore to and fro between various screens and areas.
- Advance Disclosure: Utilize moderate exposure strategies to uncover route choices steadily as clients investigate the point of interaction. Conceal optional or less significant route things behind menus or tabs to diminish mess and spotlight consideration on essential substance.
- Affordability and feedback: Give visual input and affordances to demonstrate to clients when route components are intelligent and responsive. Use liveliness, changes, and viewable signs to affirm client activities and guide them through the route stream.
- Client Testing and Emphasis: Lead ease of use testing with genuine clients to distinguish trouble spots and regions for development in the route plan. Accumulate input and repeat on the plan to streamline convenience and client fulfillment over the long run.
Designers can create mobile navigation experiences that are user-friendly, efficient, and intuitive by adhering to these principles.
Best Practices for Versatile Route Streamlining
Streamlining versatile routes is pivotal for guaranteeing a smooth and instinctive client experience. To help you get the most out of your mobile navigation, follow these best practices:
- Focus on Significant Activities: Distinguish the most basic activities or content that clients are probably going to habitually get to. Place these things noticeably in the route menu or on the landing page to make them effectively available.
- Limit Route Choices: Try not to overpower clients with such a large number of route choices. Keep the menu compact by including just the most fundamental things. Think about utilizing a cheeseburger menu or folding route to conceal less significant things and diminish mess.
- Utilize Clear Names and Symbols: Utilize clear marks for route things to assist clients with figuring out their motivation. Moreover, consolidate unmistakable symbols to improve cognizance, particularly for normal activities like home, search, and settings.
- Plan for Contact Collaboration: On touch screens, create navigational elements that are simple to tap and interact with. Guarantee that buttons and connections are adequately huge to oblige finger taps and give adequate dispersing between components to forestall coincidental taps.
- Prioritize Thumb Reach: Place significant route things inside simple reach of the client's thumb, particularly for one-gave use. Orchestrate menu things and intuitive components in the lower part of the screen to limit extending and further develop ease of use.
- Use gestures sensibly: Incorporate natural motion based route to upgrade client connection. For instance, permit clients to swipe on a level plane to explore between tabs or screens, or execute pull-to-invigorate for refreshing substance.
- Give Constant Route: Keep a diligent route bar or base tab bar all through the application to furnish clients with simple admittance to center route choices. This guarantees consistency and assists clients with exploring flawlessly across various screens.
- Include Search Features: Consolidate a pursuit highlight in the route menu to empower clients to see as unambiguous substance or data rapidly. Ensure that the app's search bar is prominently displayed and easily accessible.
- Offer Context oriented Route: Redo the route menu in view of the client's specific circumstance or area inside the application. Show applicable choices or alternate routes that line up with the client's ongoing errand or work process to smooth out routes and further develop ease of use.
- Test and Emphasize: Direct ease of use testing and assemble criticism from genuine clients to distinguish regions for development in the route plan. Use investigation devices to follow client conduct and iteratively advance the route in view of information driven bits of knowledge.
By executing these accepted procedures, you can advance versatile routes to upgrade ease of use, smooth out client travels, and work on in general fulfillment with your application or site.
Popular Versatile Route Examples
A few well known versatile route designs have arisen throughout the long term, each offering novel advantages and contemplations. Here are likely the most notable ones:
- Burger Menu: This example includes a three-line symbol (looking like a burger) that extends to uncover a secret route menu when tapped. It's space-productive and keeps the connection point clean, yet it might conceal route choices, prompting discoverability issues.
- Tab Bar Route: Tab bars are industrious route bars situated at the lower part of the screen, normally highlighting symbols addressing various segments or functionalities of the application. This example gives fast admittance to essential route choices and keeps up with perceivability all through the application.
- Base Route Cabinet: Like tab bar route, base route drawers show route choices at the lower part of the screen. On the other hand, rather than utilizing tabs, it makes use of a drawer that can be expanded to display additional options or actions.
- Drifting Activity Button (FAB): FAB is a round button generally positioned at the base right corner of the screen. It frequently addresses the essential activity in the application, like creating another message or adding another thing. FAB can provide quick access to frequently used features, but it should be used sparingly to keep the system from getting cluttered.
- Swipe Route: Swipe route permits clients to explore between various screens or segments of the application by swiping evenly. It's natural and signal based, making it appropriate for one-gave use. Nonetheless, it's fundamental to give obvious prompts to show swipe ability and keep up with consistency in route stream.
- Merry go round Route: Merry go round route presents content or highlights in a flat merry go round design, permitting clients to swipe left or right to investigate. It's outwardly captivating and proficient for exhibiting numerous things or classes, however it might require obvious signs to direct clients through the merry go round.
- Navigation on the whole screen: Full-screen route conceals the route bar and other UI components when clients look down, augmenting screen land for content. It gives a vivid encounter yet may expect clients to look back up to get to route choices.
- Looking over Route: Looking over route uses looking as an essential strategy for route, where clients can scroll upward through a solitary page design to get to various segments or content. It's basic and natural however may not be reasonable for applications with complex route structures.
- Drawer Management: Cabinet route includes a secret board that slides in from the side of the screen when set off, regularly by tapping a menu symbol or swiping from the edge. It's flexible and can oblige different route choices and settings however may expect clients to become familiar with the signal or area of the cabinet.
- Logical Route: Context oriented route powerfully changes route choices in view of the client's unique circumstance or current assignment, giving important choices and alternate ways. By displaying only the most relevant navigation options at any given time, it improves usability and efficiency.
These route examples can be consolidated or redone in view of the particular necessities and inclinations of your application or site, eventually expecting to give clients a consistent and natural route insight.
Speed Optimization for Mobile Devices
Speed improvement for cell phones is vital for conveying a smooth and responsive client experience. Here are a few systems to improve the speed of portable sites and applications:
- Upgrade Pictures and Media: Pack pictures and recordings to decrease document sizes without compromising quality. Utilize responsive pictures and sluggish stacking methods to possibly stack media when it's required, limiting introductory page load times.
- Reduce HTTP request volume: Decrease the quantity of HTTP demands by consolidating CSS and JavaScript documents, involving CSS sprites for symbols and little pictures, and keeping away from unnecessary utilization of outer assets. This smoothes out the stacking system and lessens inactivity.
- Empower Program Storing: Influence program storing by setting fitting reserve headers for static assets like pictures, CSS, and JavaScript documents. Cached copies of resources can be stored locally by browsers as a result, reducing the need for multiple downloads on subsequent visits.
- Execute Content Conveyance Organizations (CDNs): Use CDNs to circulate content across geologically scattered servers, guaranteeing quicker conveyance to clients no matter what their area. CDNs reserve static substance and serve it from the closest server, decreasing inactivity and further developing stacking times.
- Minify and Gzip Records: Minify CSS and JavaScript documents to eliminate pointless whitespace, remarks, and organizing, lessening record sizes. Moreover, empower Gzip pressure to additionally decrease the size of text-based assets moved over the organization, further developing burden times.
- Improve the response time of the server: Utilizing faster web hosting infrastructure, optimizing database queries, and caching mechanisms all have the potential to shorten server response times. Prioritize delivering content to users efficiently and reduce unnecessary server-side processing.
- Focus on Toward the top Substance: Load basic around the top substance first to guarantee that clients consider significant substance to be rapidly as could be expected. Postpone stacking superfluous substance or contents that are not quickly apparent to clients to focus on apparent execution.
- Utilize Non Concurrent Stacking: Asynchronously load scripts to stop them from preventing the page from being rendered. Offbeat stacking permits other page components to keep stacking while scripts are brought, working on by and with large responsiveness.
- Improve the Performance of JavaScript and CSS: Compose effective CSS and JavaScript code to limit delivering and execution times. Keep away from pointless DOM controls, diminish the utilization of complicated selectors, and streamline JavaScript capabilities for better execution on cell phones.
- Test and Screen Execution: Routinely test the presentation of your versatile site or application utilizing apparatuses like Google PageSpeed Bits of knowledge, Beacon, or WebPageTest. To identify areas for improvement and ensure ongoing optimization, monitor key performance metrics like page load time, time to interactive, and server response time.
You can improve the performance of your mobile website or application by implementing these speed optimization strategies, allowing users to enjoy faster loading times and smoother browsing on their devices.
All in all, portable improved route designs address a basic part of contemporary computerized plan, especially in a period where cell phones have become pervasive devices for getting to online substance. Designers can effectively address the unique challenges posed by mobile browsing, such as touch-based interactions and limited screen real estate, by prioritizing seamless user experiences tailored to smaller screens. Whether through natural signals, working on menus, or creative route structures, these examples mean to upgrade ease of use and openness while keeping up with consistency across gadgets. In addition to ensuring a more user-friendly experience, adopting mobile-optimized navigation demonstrates a commitment to meeting the ever-evolving requirements and expectations of mobile users. As portable keeps on overwhelming computerized connections, incorporating these route designs into plan methodologies becomes fundamental for making drawing in and easy to use encounters that reverberate with crowds around the world.
Recent Stories
500k Customer Have
Build a stunning site today.
We help our clients succeed by creating brand identities.
Get a Quote