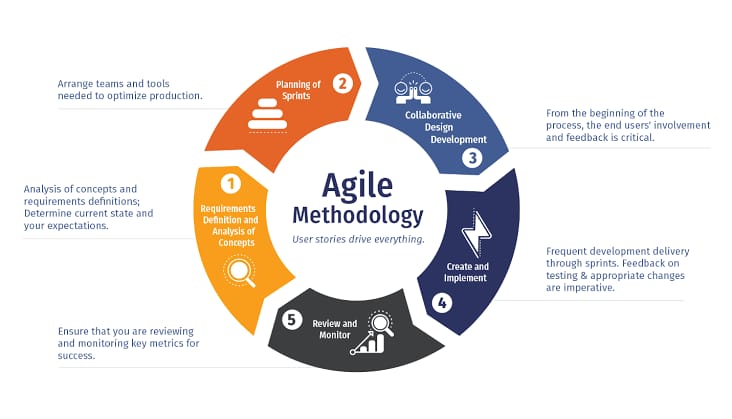
The Impact of UI/UX Design on User Engagement

In the present computerized scene, the progress of an item or administration pivots essentially on its UI (UI) and Client Experience (UX) plan. These aspects go beyond merely aesthetics; They fundamentally influence how digital product users interact with and evaluate them. A mundane interface can be transformed into an engaging and intuitive experience through effective UI/UX design, influencing user engagement and satisfaction directly. Understanding the profound impact of UI/UX on user engagement becomes essential for creating products that not only attract users but also retain them, fostering loyalty and driving sustained growth as businesses increasingly recognize the importance of user-centric design.
This is an outline of the way UX/UX configuration influences client commitment:
1. First Impressions
- Appeal to the Eye: The first impression is made by a product's visual design. Appealing and current plans can charm clients, making them bound to remain and investigate.
- Image of the Brand: A well-designed UI/UX projects professionalism and dependability, reflecting positively on the brand.
2. Traversability Convenience: If a website's navigation is straightforward and user-friendly, users are less likely to become dissatisfied and more likely to continue using the site.
- Learnability: Clients feel more quiet and certain utilizing the item when it has an easy to understand plan with clear directions and supportive tips.
3. Openness
- Inclusivity: Available plan guarantees that clients with incapacities can utilize the item, widening the client base and upgrading in general commitment.
- Design that Responds: An item that works flawlessly across various gadgets (work areas, tablets, cell phones) guarantees predictable client experience, empowering clients to connect all the more much of the time.
4. Positive Interactions: Emotional Connection Miniature corporations, movements, and input can make the client experience charming, encouraging a positive close to home association with the item.
- Personalization: Enhancing user engagement is personalized content and customizable interfaces that make users feel valued and understood.
5. Execution and Productivity
- Load Time: As sluggish performance can cause dissatisfaction and abandonment, fast loading times are essential for user retention.
- Task Effectiveness: All around planned work processes and assignment mechanization further develop proficiency, permitting clients to achieve their objectives rapidly and with insignificant exertion.
6. Support and Feedback
- Clear Feedback: Users are better able to comprehend the outcomes of their interactions when prompt and clear feedback for their actions is provided, reducing errors and confusion.
- Systematic Support: By providing assistance when required, integrated support options like chatbots, help centers, and frequently asked questions improve the user experience.
7. Hooks for User Retention and Engagement: Highlights like notices, updates, and gamification components make clients want more.
- Satisfaction: A positive user experience boosts overall satisfaction, which in turn increases retention rates and promotes by word of mouth.
Importance of Intuitive Navigation
Natural route assumes a vital part in different parts of plan, especially in computerized connection points like sites, applications, and programming. Intuitive navigation is critical for the following reasons:
- Improved UX (User Experience): Natural route makes it easier for customers to find what they need quickly and effectively, which directly contributes to a positive customer experience. Clients are bound to be happy with an item or administration on the off chance that they can explore it without getting lost or disappointed.
- Reduced ability to absorb information: Intuitive course diminishes the time and effort clients need to sort out some way to use a structure. New users are able to quickly comprehend how to navigate the interface when elements are logically placed and labeled in accordance with user expectations.
- Expanded Commitment: A platform with simple navigation is more likely to engage users. They spend more time interacting with content or performing tasks rather than figuring out how to move around, which results in higher engagement rates.
- Lower Bob Rates: Sites with befuddling routes frequently have higher bob rates (clients leaving the site rapidly subsequent to showing up). Natural route urges clients to investigate further, decreasing skip rates and improving the probability of transformations or accomplishing different objectives.
- Upholds Openness: Clear route is fundamental for openness, assisting clients with disabilities explore the point of interaction all the more actually. All users, including those who use assistive technologies, benefit from features like consistent structure, descriptive labels, and menus that are simple to access.
- Image of the Brand: A brand's professionalism and attention to user needs are reflected positively by intuitive navigation. As users feel that their time and experience are valued, it can improve brand perception and build trust.
- Consistency across devices: In the present multi-gadget climate, natural route guarantees consistency across various stages (e.g., work area, portable, tablet). Clients expect a comparable encounter paying little mind to how they access the assistance, and the instinctive route keeps up with this rationality.
- Works with Errand Fulfillment: Whether it's making a buy, tracking down data, or communicating with content, instinctive route smoothes out the way to finishing responsibilities. The achievement of business goals and user satisfaction depend on this efficiency.
- In conclusion, developing a digital experience that is both effective and user-friendly necessitates clear and simple navigation. It upholds ease of use, upgrades commitment, lessens rubbing, and eventually adds to the general progress of an item or administration in the computerized scene.
Creating Persuasive Call-to-Action Buttons
It is essential to make persuasive call-to-action (CTA) buttons in order to direct users to take particular actions on digital interfaces, apps, or websites. Here are a few critical systems to make your CTAs more powerful and convincing:
- Clear and Activity Arranged Text: Use language that is clear, action-oriented, and concise about what users should anticipate when they click the button. Use, for instance, "Get Started," "Sign Up Now," or "Explore Plans" in place of "Submit."
- Accentuate the Value Proposition: Make it abundantly clear to users what they will gain from clicking the CTA button. For instance, the phrases "Save 20% Today" and "Download Your Free Ebook" make it abundantly clear to customers what they stand to gain from participating.
- Give yourself a sense of urgency: Use words that make you feel like you need to act right away to encourage that. expressions, for example, "Act Currently," "Restricted Time Offer," or "Just 3 Remaining!" can entice users to press the button immediately.
- Use Separating Assortments: Utilize a variety of differentiations with the foundation to guarantee that the CTA button stands apart on the page. The button is bound to be seen and clicked along these lines, which helps cause you to notice it.
- Change the Button's Size and Position: Check to see that the button is large enough to be easy to click without taking up too much room on the page. Users naturally look for it when they are ready to take action, so it should be strategically placed after important information or at the end of a section that is focused on conversion.
- Make it appealing to the eye: Configuration matters with regards to CTAs. Use buttons that look good and make people want to click on them. The button can look more interactive and appealing if it has rounded corners, subtle shadows, or hover effects.
- Offer Social Evidence: To reassure users and build trust, include social proof near the CTA button, if necessary. For example, "Appraised 5 stars by our clients" or "Join 10,000+ fulfilled clients."
- Test and Stress: Make use of A/B testing to experiment with a variety of CTA variants (text, position, and so on). to ascertain which ones perform best. To improve conversion rates, iterate on a regular basis based on data and user feedback.
- Versatile Enhancement: Guarantee your CTAs are completely improved for cell phones, where clients might collaborate diversely contrasted with work area clients. On smaller screens, buttons ought to be placed where they are effectively open and large enough for simple tapping.
- You can make influential CTAs that successfully urge clients to make the ideal moves by executing these procedures. This will result in higher conversion rates and increased user engagement on your digital platforms.
A/B Testing for UI/UX Optimization
In UI/UX improvement, a strong technique called "A/B testing" is utilized to figure out which plan varieties are more famous with clients. A good way to use A/B testing for UI/UX optimization is as follows:
1. Recognize Objectives and Measurements
- Characterize Goals: Be specific about what you want your UI/UX design to accomplish. This could mean getting more people to buy, getting fewer people to bounce, making users more engaged, etc.
- Select Metrics: Measurable metrics that are in line with your goals should be chosen. For instance, change rate, active visitor clicking percentage, time on page, or assignment culmination rate.
2. Create Hypotheses
- Generate Variations: Develop different versions (variants) of your UI elements. This could include changes in design, colors, text styles, button situations, route menus, and so forth.
- Develop Hypotheses: Based on user behavior insights, best practices, or previous testing, predict which design modifications or elements will improve performance.
3. Set Up A/B Tests
- Apparatuses and Stages: To set up experiments, either in-house solutions or A/B testing tools like Google Optimize, Optimizely, and VWO are used.
- Randomization: To ensure statistical validity and minimize bias, ensure that users are randomly assigned to various variants.
4. Run Experiments
- Duration and Traffic: Run experiments for a sufficient duration to capture diverse user behaviors and ensure statistical significance. Ensure you have enough traffic to generate meaningful results.
- Segmentation: If applicable, segment users based on relevant criteria (e.g., new vs. returning users, different demographics) to understand how different groups interact with your designs.
5. Collect and Analyze Data
- Quantitative Analysis: Analyze the collected data using statistical methods to determine which variant performs better in achieving your defined metrics.
- Qualitative Insights: Complement quantitative data with qualitative insights from user feedback, heatmaps, session recordings, and usability testing to understand why certain variants perform better.
6. Draw Conclusions
- Statistical Significance: Ensure results are statistically significant before drawing conclusions. This typically involves comparing conversion rates or other metrics with confidence intervals.
- Iterative Optimization: Based on findings, implement changes from the winning variant and iterate further to continually optimize UI/UX design.
7. Document Learnings
- Document Results: Record insights gained from A/B testing to inform future design decisions and maintain a repository of learnings for ongoing improvement.
- Share the results: Share discoveries and proposals with applicable partners to adjust on plan enhancements and approve UX methodologies.
8. Consistent Improvement
- Emphasize and Test: Utilize A/B testing as a continuous procedure to continuously refine UX/UX components in response to user feedback, prevailing trends, and business objectives.
- By utilizing A/B testing successfully in UI/UX improvement, organizations and creators can pursue information driven choices that upgrade client experience, increment commitment, and eventually drive wanted results.
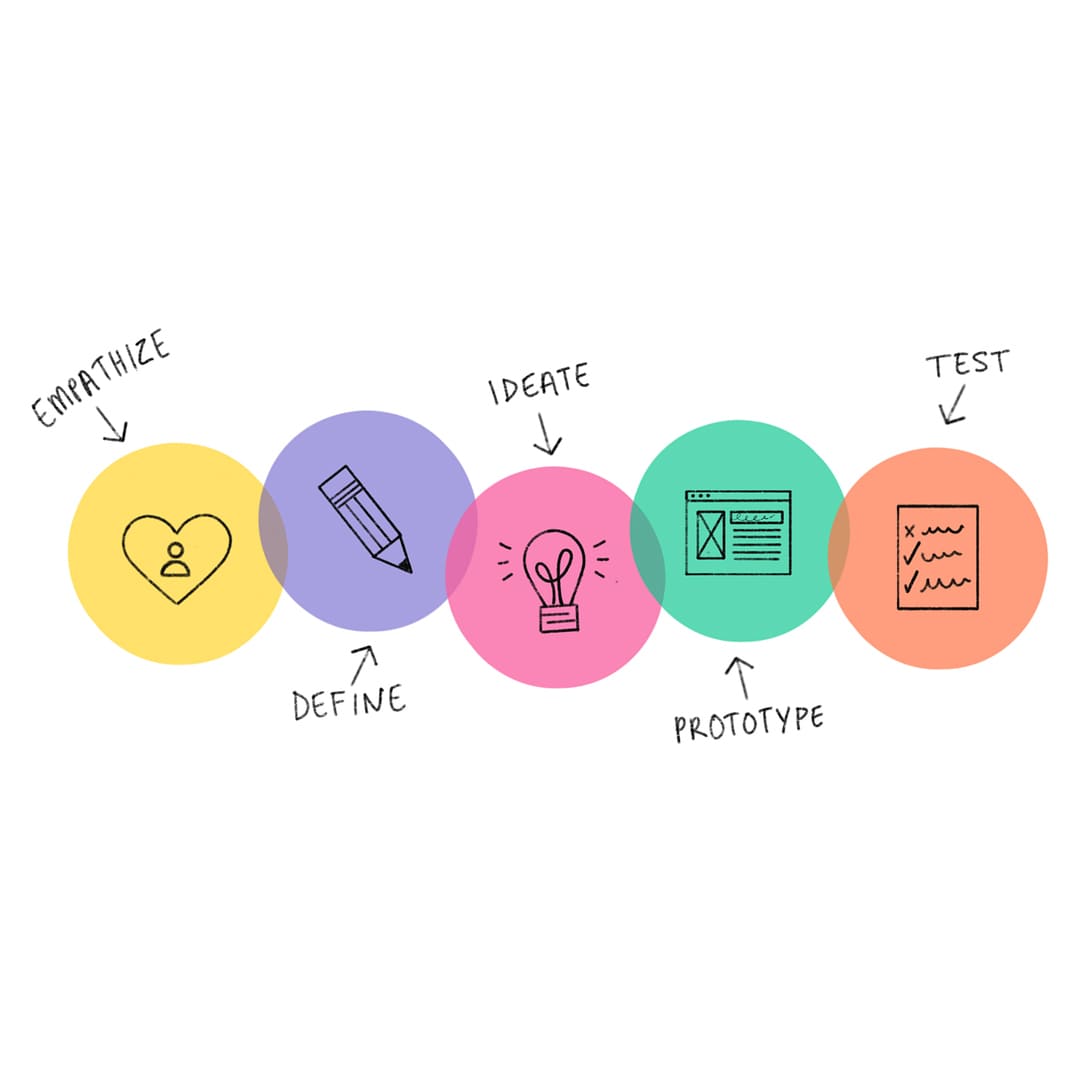
Design Thinking in the UI/UX Process
Design thinking is a human-focused technique for development and critical thinking that has arisen as a fundamental part of the interaction.
1. Empathize
- User research: Empathizing with users to comprehend their requirements, behaviors, and issues is the first step in design thinking.
- Surveys and interviews with users: Direct subjective exploration, for example, meetings and studies to acquire bits of knowledge into client objectives and difficulties.
- Persona Creation: Make personas to address different client gatherings and their inspirations, which assist with directing plan choices.
2. Define
- Issue Articulation: Using the information gathered during the empathy phase, define the issue or opportunity.
- Perspective (POV): Reframe the requirements of the user into a specific, measurable, and guiding POV statement for ideation.
- Client Excursion Planning: Identify key touchpoints and pain points by visualizing the user experience journey.
3. Ideate
- Brainstorming: Create a great many thoughts and answers to address the characterized issue.
- Drawing and Prototyping: Utilize quick prototyping methods to picture and repeat on plan ideas.
- Co-creation: Include cross-practical groups and partners in ideation meetings to cultivate imagination and various points of view.
4. Prototype
- Low-Devotion Models: Make unpleasant models to approve plan ideas and accumulate input rapidly.
- Iterative Plan: Continually improve prototypes based on test results and user feedback.
- Ease of use Testing: To identify usability issues and validate design assumptions, conduct frequent and early usability testing.
5. Test
- Client Criticism: Utilize usability testing sessions to gather qualitative and quantitative feedback from customers.
- Utilize feedback to iterate: Make use of the learnings from testing to refine and enhance the design.
- The A/B Test: Test various varieties of UI components to figure out which plans perform better in accomplishing client objectives.
6. Implement
- Collaboration: Make sure the design vision is carried out successfully by working closely with developers and other stakeholders.
- Plan Framework: To ensure product consistency and scalability, document design patterns and guidelines.
- Iterative Improvement: Proceed to repeat and work on the UI/UX in view of client criticism and developing necessities.
In conclusion, it is impossible to overstate the impact of UI/UX design on user engagement. A well-crafted UI/UX design improves usability, fosters emotional connection, and facilitates efficient interactions in addition to aesthetics and functionality. Businesses can create digital experiences that not only initially attract users but also maintain their engagement over the course of time by prioritizing the needs and preferences of users. Putting resources into UI/UX plan further develops consumer loyalty and devotion as well as yields substantial business benefits, including expanded change rates, higher maintenance, and positive brand discernment. As innovation advances and client assumptions keep on rising, the job of UI/UX configuration will stay critical in molding fruitful computerized items and administrations in the serious scene of today and tomorrow.
Recent Stories
500k Customer Have
Build a stunning site today.
We help our clients succeed by creating brand identities.
Get a Quote